The Ultimate Guide to Pharmaceutical Packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging plays a critical role in the healthcare industry, ensuring that medicines are safely delivered to consumers. It not only protects the integrity of the medication but also provides crucial information for proper usage and compliance.
This comprehensive guide delves into the types, benefits, and essential machinery involved in pharmaceutical packaging, providing valuable insights for industry professionals.

Pharmaceutical packaging: an overview
What is pharmaceutical packaging?
Pharmaceutical packaging encompasses the processes and materials used to encase medications, ensuring their protection, stability and delivery. It covers a broad range of packaging solutions, from primary containers like bottles and blister packs to secondary and tertiary packaging for storage and transportation.
Regulatory standards and compliance:
Regulatory standards are paramount in pharmaceutical packaging. Packaging must comply with guidelines set by regulatory bodies such as the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) in the UK, the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other local health authorities. These regulations ensure that packaging materials are safe, non-reactive and capable of maintaining the integrity of the medications.
Types of pharmaceutical packaging
Primary packaging:
Primary packaging is the first layer of packaging that comes in direct contact with the medication. This includes bottles, blister packs, ampoules and vials. The primary purpose is to protect the drug from contamination, degradation and damage.
Secondary packaging:
Secondary packaging encompasses additional layers that group primary packages together. This includes cartons and boxes that provide extra protection and facilitate handling and distribution.
Tertiary packaging:
Tertiary packaging is used for bulk handling and transport. Pallets and large containers fall under this category, ensuring the safe shipment of pharmaceuticals from manufacturing sites to distribution centres and pharmacies.
Pharmaceutical packaging machines:
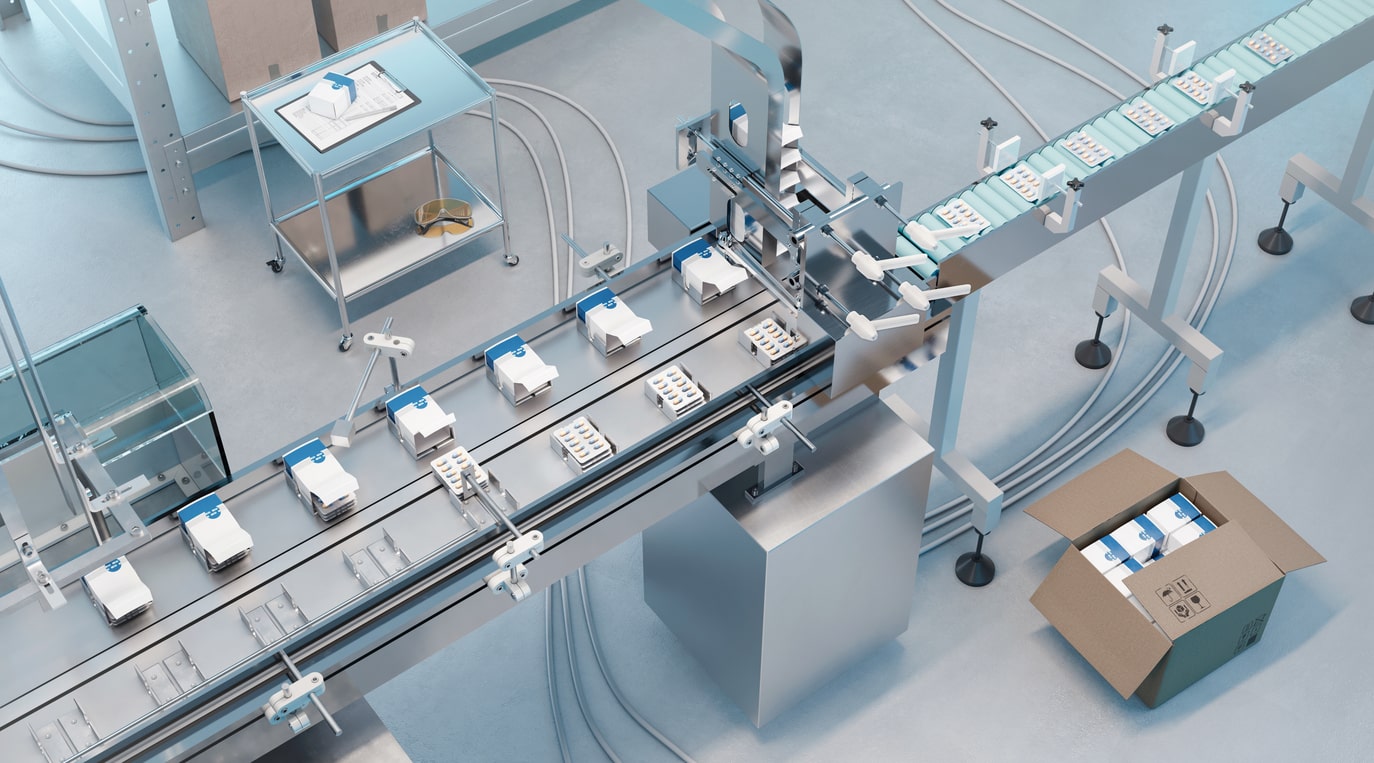
Efficient and reliable pharmaceutical packaging requires sophisticated machinery. These machines streamline the packaging process, ensuring precision and compliance with stringent standards.

End-of-line equipment for pharmaceutical packaging:
End-of-line equipment is essential for final packaging stages, including wrapping, cartoning and palletising. This equipment ensures that pharmaceutical products are securely packed and ready for distribution. Common applications include wrapping multiple boxes of blister packs, cartoning bottles of liquid medications and palletising cases of medical supplies.
Bottle filling, capping and labelling equipment for pharmaceuticals
Bottle filling, capping and labelling equipment are crucial for packaging liquid medications. These machines ensure accurate dosing, secure sealing and clear labelling of pharmaceutical bottles. They are used for products such as syrups, liquid antibiotics and over-the-counter cough medicines.
Sachet packing machines in pharmaceutical packaging:
Sachet packing machines are ideal for packaging powders, granules and liquids in small, single-dose packets. These machines ensure precise filling and sealing, crucial for maintaining medication integrity. They are commonly used for products like rehydration salts, powdered vitamins and single-use antiseptic solutions.
Stick packaging machines for pharmaceuticals:
Stick packaging machines offer a convenient way to package single-dose pharmaceuticals in slender, easy-to-use sticks. They are particularly useful for products like powdered supplements, energy boosters and flavour enhancers for medications.
Pouch filling machines in pharmaceutical packaging:
Pouch filling machines are versatile and capable of packaging a variety of pharmaceutical forms, from liquids to solids. These machines ensure the integrity and safety of the contents. Typical applications include packaging topical creams, oral rehydration solutions and nutritional supplements.
Flow wrap machines for pharmaceuticals:
Flow wrap machines are used for high-speed wrapping of individual items, providing a tight and protective seal. Flow wrapping is ideal for packaging items like blister packs, medical devices and single-use medical instruments.
Benefits of pharmaceutical packaging:
Product protection:
Pharmaceutical packaging protects medications from environmental factors such as moisture, light and oxygen, which can degrade the product. Proper packaging ensures the stability and efficacy of medications.
Patient safety:
Effective packaging prevents contamination and ensures the correct dosage is delivered. Features such as tamper-evident seals and child-resistant closures enhance patient safety by preventing accidental ingestion and tampering.
Compliance and traceability:
Packaging that adheres to regulatory standards helps ensure compliance. Traceability features such as barcodes and radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags allow for tracking and verification of products throughout the supply chain, reducing the risk of counterfeit drugs.
Brand integrity:
High-quality packaging reflects the brand’s commitment to quality and safety, building consumer trust. Attractive and functional packaging also enhances the user experience and promotes brand loyalty.
Advanced technologies in pharmaceutical packaging:
Smart packaging:
Smart packaging incorporates technology such as QR codes and NFC tags that provide additional information and interactivity. These features can offer patients detailed usage instructions, reminders and product authentication.
Tamper-evident features:
Tamper-evident packaging ensures that any unauthorised access to the medication is easily detectable. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of pharmaceuticals.
Child-resistant packaging:
Child-resistant packaging is designed to prevent children from accessing harmful medications while remaining accessible to adults. This type of packaging is mandated for certain types of pharmaceuticals.
Sustainable packaging solutions:
Eco-friendly materials:
Using recyclable and biodegradable materials in pharmaceutical packaging reduces environmental impact. Eco-friendly packaging solutions are becoming increasingly important as companies strive to meet sustainability goals.
Reducing carbon footprint:
Implementing sustainable practices in packaging production, such as reducing material usage and optimising logistics, helps lower the carbon footprint of pharmaceutical packaging operations.
Challenges in pharmaceutical packaging:
Regulatory challenges:
Navigating the complex landscape of global regulatory requirements can be challenging. Companies must stay informed about changing regulations and ensure their packaging complies with all relevant standards.
Technological challenges:
Adopting new technologies in packaging can be costly and require significant investment in equipment and training. Ensuring compatibility and maintaining the quality of packaging are ongoing challenges.
Supply chain issues:
Disruptions in the supply chain, such as material shortages or transportation delays, can impact the availability and cost of pharmaceutical packaging materials.
Future trends in pharmaceutical packaging:
Automation and AI in pharmaceutical packaging:
The integration of automation and AI in pharmaceutical packaging processes enhances efficiency and accuracy. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks with precision, reducing the risk of human error.
Personalised medicine packaging:
With the rise of personalised medicine, packaging solutions are evolving to accommodate individualised treatment plans. Customisable packaging that can be tailored to specific patient needs is becoming more prevalent.
Innovative solutions:
Pharmaceutical packaging is a critical component of the healthcare industry, ensuring the safety, efficacy and compliance of medications. Advances in technology and sustainability are shaping the future of pharmaceutical packaging, offering innovative solutions to meet the evolving needs of the industry. By understanding the types, benefits and challenges of pharmaceutical packaging, companies can make informed decisions that enhance product integrity and patient safety.
FAQs:
What is pharmaceutical packaging?
Pharmaceutical packaging refers to the process of enclosing medications in protective materials to ensure their safety, stability and proper delivery to consumers.
What are the types of pharmaceutical packaging?
The main types of pharmaceutical packaging are primary, secondary and tertiary packaging. Primary packaging directly contacts the drug, secondary packaging provides additional protection and tertiary packaging is used for bulk handling and transportation.
Why is pharmaceutical packaging important?
Pharmaceutical packaging is essential for protecting medications from environmental factors, ensuring patient safety, maintaining compliance with regulations and preserving brand integrity.
What are the benefits of using pharmaceutical packaging machines?
Pharmaceutical packaging machines offer precision, efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards. They streamline the packaging process, reduce the risk of contamination and ensure accurate labelling and dosage.
What are the latest trends in pharmaceutical packaging?
Current trends in pharmaceutical packaging include the use of smart packaging, tamper-evident features, child-resistant packaging and sustainable materials. Automation and AI are also becoming increasingly prevalent.
How can pharmaceutical packaging be made more sustainable?
Sustainability in pharmaceutical packaging can be achieved by using eco-friendly materials, reducing material usage, optimising logistics and enhancing recycling processes.
For more detailed information or enquiries, feel free to contact Omori.

